Digital advertising thrives on key performance metrics, and one of the most critical benchmarks is CPM (Cost Per Thousand Impressions). Whether you’re a brand aiming to expand visibility or an advertiser managing campaigns, understanding CPM can empower you to optimize resources and achieve measurable results.
Visual breakdown of CPM components.
What is CPM?
At its core, CPM measures the cost of 1,000 ad impressions—a single impression being counted each time an ad appears on a screen, regardless of interaction. This pricing model is widely used in display advertising, programmatic ads, and video ads, making it a cornerstone for campaigns aimed at maximizing reach.
The Formula for CPM
The CPM calculation is straightforward:
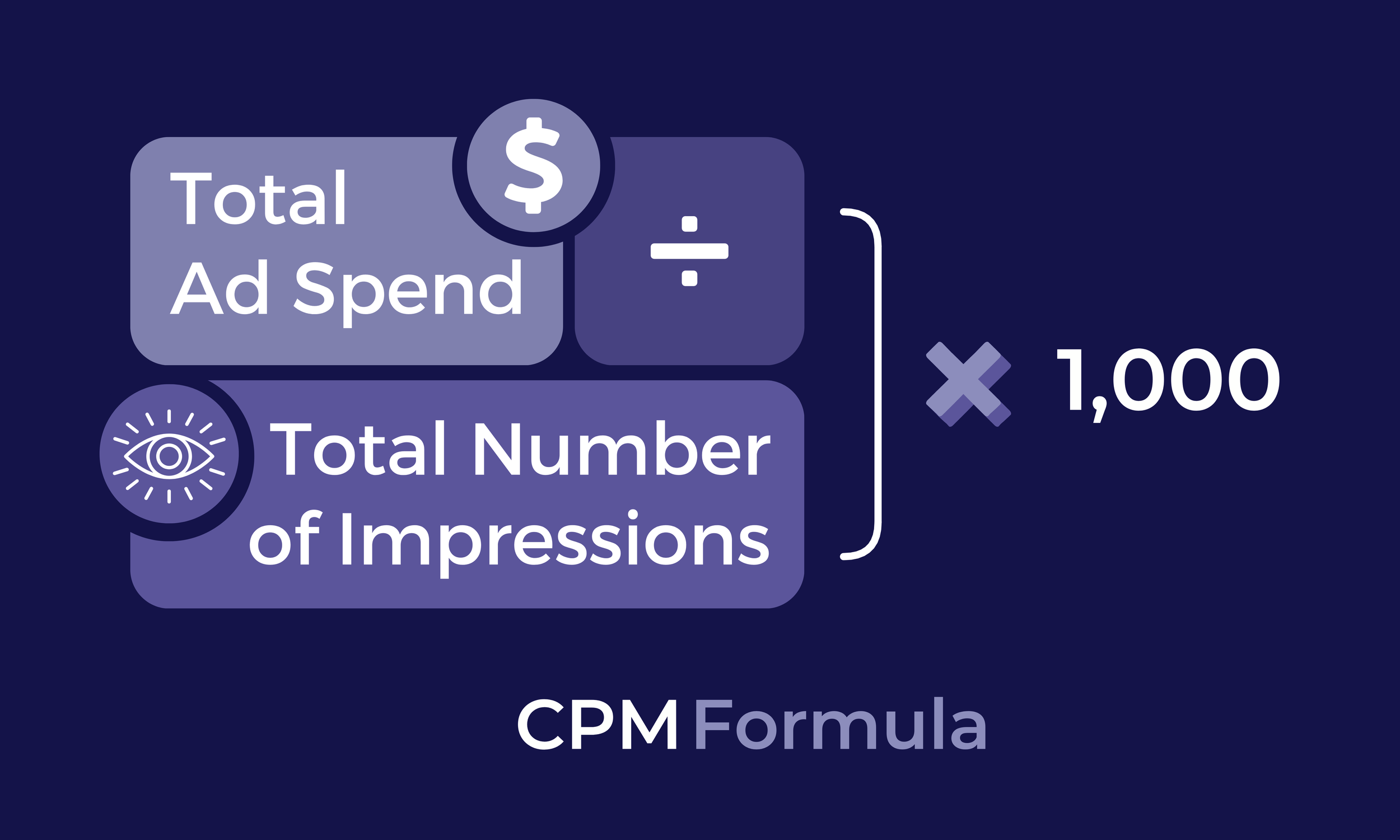
CPM = ( frac{text{Cost of Ad Campaign}}{text{Number of Impressions}} times 1,000 )
For example, if you spend $500 on a campaign and achieve 200,000 impressions:
CPM = ( frac{500}{200,000} times 1,000 ) = $2.50
This means you’re paying $2.50 for every 1,000 people who see your ad.
Why is CPM Important?
CPM serves as a foundation for understanding campaign efficiency and planning budgets for advertising strategies. Here are some benefits:
- Scalability: Ideal for campaigns focused on brand awareness where reaching a larger audience matters more than direct actions.
- Comparability: CPM provides a consistent metric to compare performance across platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and traditional media.
For an in-depth understanding of CPM, Investopedia’s Guide offers excellent insights.
How CPM Works
Use Cases Across Industries
CPM finds application across diverse advertising mediums, such as:
- E-commerce Websites: Promoting seasonal sales to wide audiences.
- Media Platforms: Boosting video views or article impressions.
- Mobile Advertising: Driving app installs via large-scale promotions.
Each use case underlines CPM’s role as a flexible and efficient model for spreading awareness.
Example of CPM in e-commerce campaigns.
Factors Influencing CPM
Several variables impact CPM rates, including:
- Audience Demographics: Ads targeting niche groups often incur higher costs.
- Ad Placement: Premium positions on websites or platforms drive up CPM.
- Seasonality: Costs increase during peak advertising periods like holidays.
“Understanding your audience and strategic placements can significantly lower CPM while ensuring quality impressions.”
Advantages of CPM
For marketers, CPM presents several advantages over other models like CPC (Cost Per Click) or CPA (Cost Per Action):
- Cost Efficiency: CPM is often cheaper than CPC, especially for campaigns that do not require user engagement but prioritize visibility.
- Simplicity in Budgeting: The clear-cut formula makes forecasting expenses straightforward.
- Maximized Reach: Advertisers can target millions of impressions across multiple platforms.
Comparing CPM with Other Models
Consider these comparisons:
| Metric | Purpose | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| CPM | Broad reach | Brand awareness campaigns |
| CPC | Interaction-focused | Driving website traffic |
| CPA | Conversion-driven | Sales or leads |
Comparing CPM with CPC and CPA models.
Challenges of CPM
While CPM offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges:
- Impression Quality: Not all impressions guarantee visibility. Some may occur on areas with low audience attention.
- Fraudulent Traffic: Ad fraud, such as bots inflating impressions, can distort CPM metrics.
- Low Engagement Rates: Unlike CPC, CPM does not factor in click-through rates (CTR) or other user interactions.
“Advertisers need robust analytics tools to monitor campaign quality and ensure valid impressions.”
For effective solutions, AdPushup’s Tips provide guidance on tackling these obstacles.
Would you like the remaining sections, including strategies to optimize CPM, the future of CPM, or examples?
Strategies to Optimize CPM
Maximizing the value of CPM campaigns requires careful planning and the implementation of effective strategies. Here’s how to ensure your advertising dollars yield the best results:
1. Target the Right Audience
Precise audience segmentation is critical for increasing impression quality. Use tools like Google Analytics or Facebook Audience Insights to identify your ideal customer demographics, behaviors, and interests.
- Segment your audience by location, age, and interests.
- Run A/B tests to refine which segments respond best to your ads.
“The more relevant your ads are to your audience, the higher the value of each impression.”
2. Invest in Premium Ad Placements
Not all impressions are created equal. High-visibility placements, such as banners on premium websites or top-of-feed spots on social media, can significantly improve your CPM performance.
Visualizing strategic ad placements for optimal CPM.
3. Focus on Ad Quality
Compelling visuals and engaging copy make a huge difference in your ad performance. Follow these best practices:
- Use eye-catching visuals and bold headlines.
- Incorporate video ads, as they tend to have higher engagement rates than static images.
- Ensure mobile optimization, as a significant percentage of impressions occur on smartphones.
4. Leverage Data Analytics
Monitor your campaigns closely to identify trends and areas for improvement. Key metrics to track include:
- Impressions Delivered: Are you reaching your desired audience?
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): Even though CPM focuses on impressions, a higher CTR indicates better engagement.
- Frequency: Avoid oversaturating your audience by limiting the frequency of impressions.
Tools like Google Ads Manager, Taboola, or Outbrain provide in-depth analytics that can help you refine your campaigns.
The Future of CPM
As the digital landscape evolves, CPM is adapting to new trends and technologies. Here’s what to expect in the coming years:
AI and Programmatic Advertising
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming CPM campaigns by enabling real-time bidding and precise targeting. Programmatic advertising platforms such as The Trade Desk or Adobe Advertising Cloud use AI to maximize campaign efficiency.
Mobile and Video Advertising
Mobile devices and video ads are set to dominate the CPM landscape. With more users consuming content on mobile platforms, advertisers are focusing heavily on formats like vertical video and interactive ads.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics will allow advertisers to forecast campaign performance based on historical data. This means smarter budget allocation and more strategic planning.
“Embracing these advancements will help advertisers stay ahead in a competitive digital marketplace.”
FAQs About CPM
What is a good CPM rate?
A good CPM rate varies depending on the industry and platform. On average:
- $5–$10: Display ads on social media platforms.
- $20–$50: High-quality placements on premium websites.
How can I reduce my CPM costs?
To lower CPM costs:
- Refine your target audience to avoid irrelevant impressions.
- Focus on ad quality and placement optimization.
- Monitor performance and adjust strategies accordingly.
Is CPM better than CPC?
It depends on your campaign goals:
- Choose CPM for brand awareness campaigns with a broad audience.
- Opt for CPC if driving website traffic or conversions is your priority.
Conclusion
CPM remains a vital metric in the digital advertising ecosystem, offering a reliable way to measure and optimize campaign reach. By implementing the strategies outlined above, businesses can maximize the effectiveness of their ad spend and achieve measurable brand growth.
For more insights on digital advertising metrics, explore resources like AdPushup’s Blog or FasterCapital’s Guide.
Start optimizing your CPM campaigns today and unlock their full potential!
